symbols
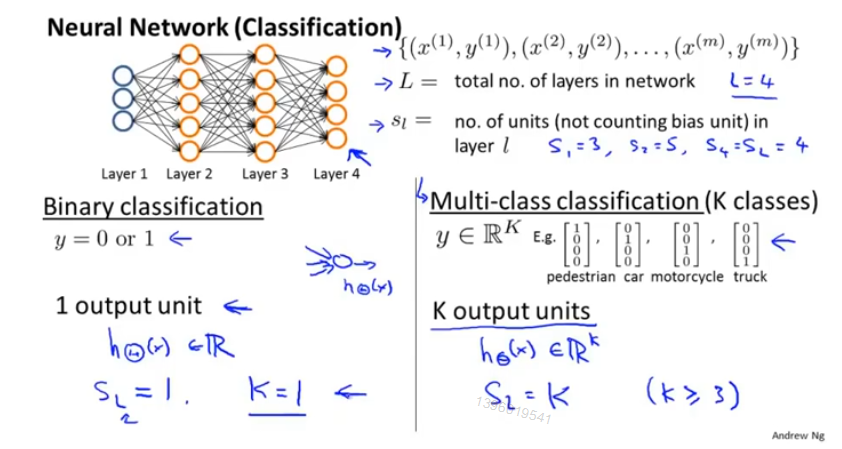
L : 神经网络的层数
S_l : 第 l 层神经网络的神经元数
K :分类个数
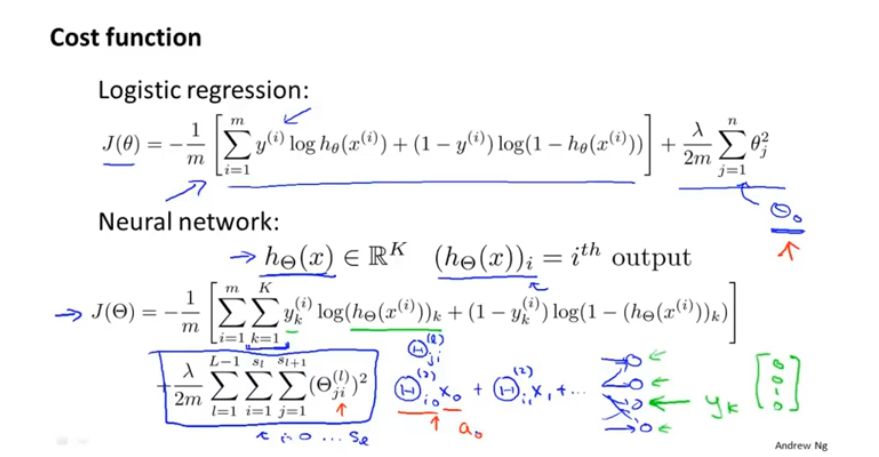
代价函数
从逻辑回归算法中衍生到神经网络
每个 logistic regression algorithm 的代价函数 然后 K次输出 最后求和。
不对偏置单元(bias)进行正则化操作,即含X_0的项
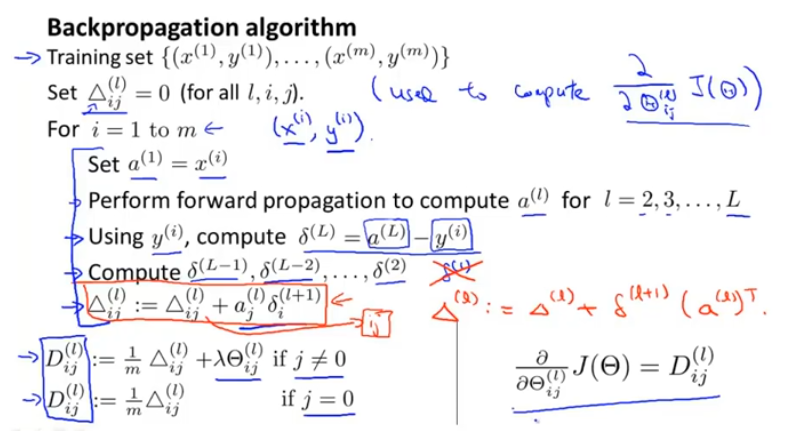
步骤
定义:误差项 delta(l)_j 表示第 l 层的第 j 的激活值与y之间的误差。
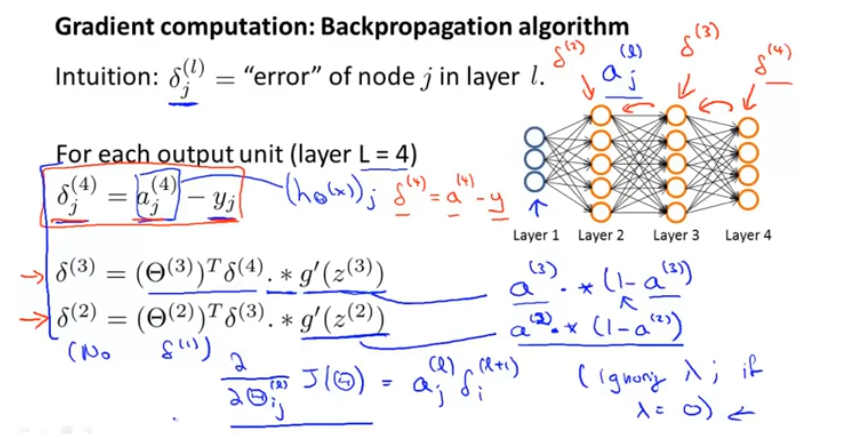
不严谨地说 :在忽略lambda(正则项)或lambda=0,误差项 = 相应的代价项的偏导 由此可以计算出所需参数。
综上:
▲是大写的delta
更好地理解
delta(l)_j 其实是代价函数关于Z(l)__j的偏导,其值只计算隐藏单元而不计算偏置单元。

参数
矩阵与向量
公式中参数的形式均为向量,所以需要将矩阵转化为向量形式。
矩阵->向量: a = [ b1(:); b2(:); b3(:) ]
向量->矩阵: b1 = reshape(a(1:110),10,11); %向量前110个数组成10行11列的矩阵。

梯度检测
(1)梯度估计
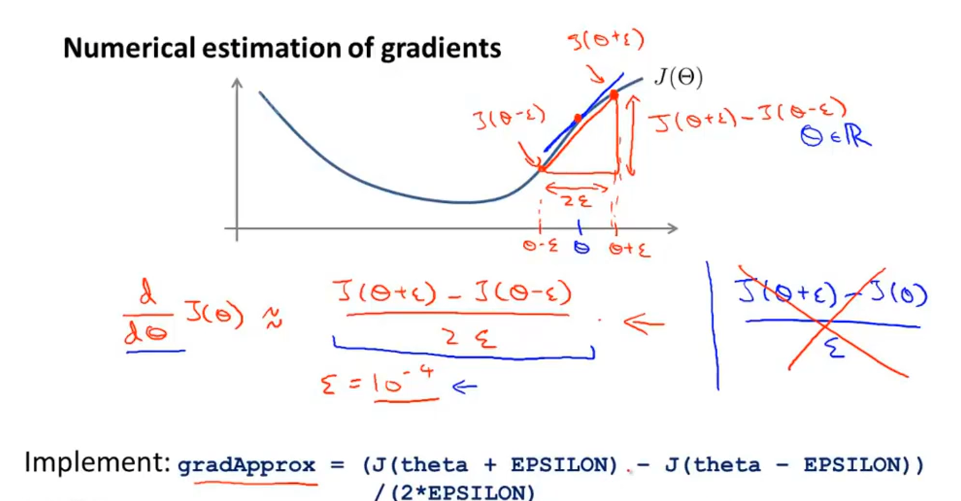
(2)J(θ)偏导数
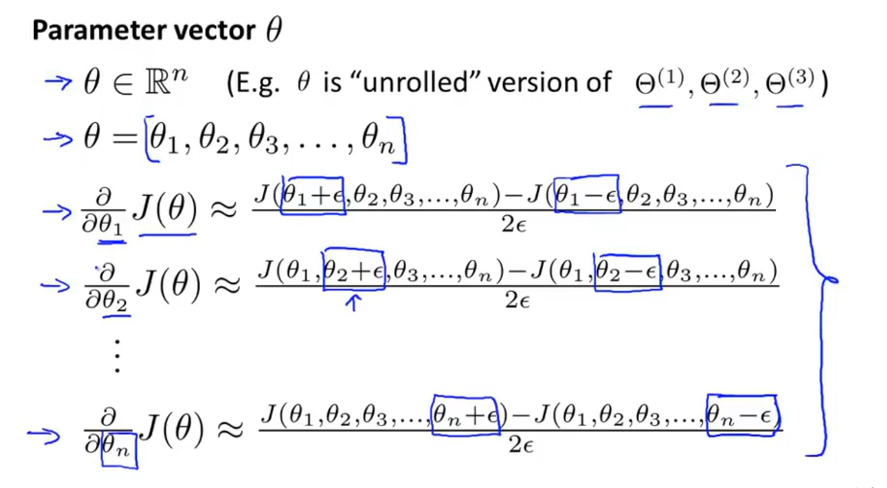
(3)检查J(θ)偏导数 是否等于 反向传播的导数,近似相等则反向传播正确实现

综合检测步骤:
注意在正确之后,关闭梯度检测再进行训练分类器。

θ随机初始化
防止 θ值相同,限制学习模型的特征输入
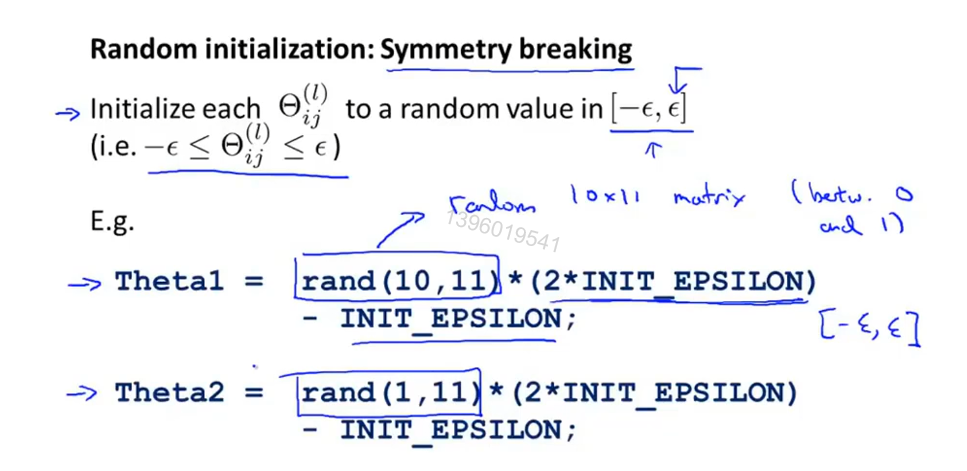
总结
训练神经网络
(1)选择网络架构: 输入特征项数,输出分类项 ,隐藏层(1个或者 多个但每层隐藏单元相同)
(2)随机初始化θ
(3)完成前向传播算法得到h_θ(x)
(4)完成代价函数 J(θ) 的计算
(5) 完成反向传播算法得到 J关于θ的偏导数
(6)遍历训练集,运行前向传播算法和反向传播算法,得到每层激活项a(l)与delta(l)
(7)梯度检查
(8)高级优化算法与反向传播算法结合计算min J.
编程作业
nnCostFunction.m
1 | function [J grad] = nnCostFunction(nn_params, ... |
sigmoidGradient.m
1 | function g = sigmoidGradient(z) |
randInitializeWeights.m
1 | function W = randInitializeWeights(L_in, L_out) |