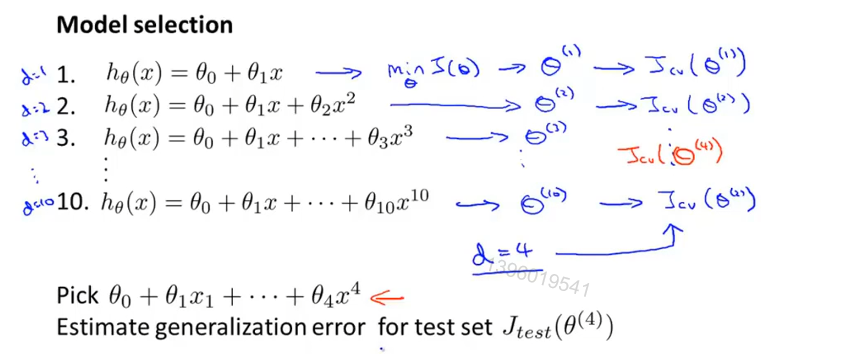
模型选择
60% 训练集 20%验证集 20%测试集
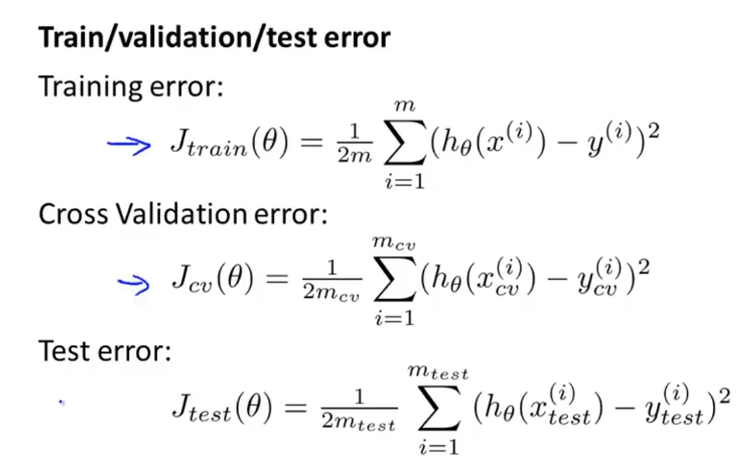
训练集计算误差,利用交叉验证集选择维数,泛化能力
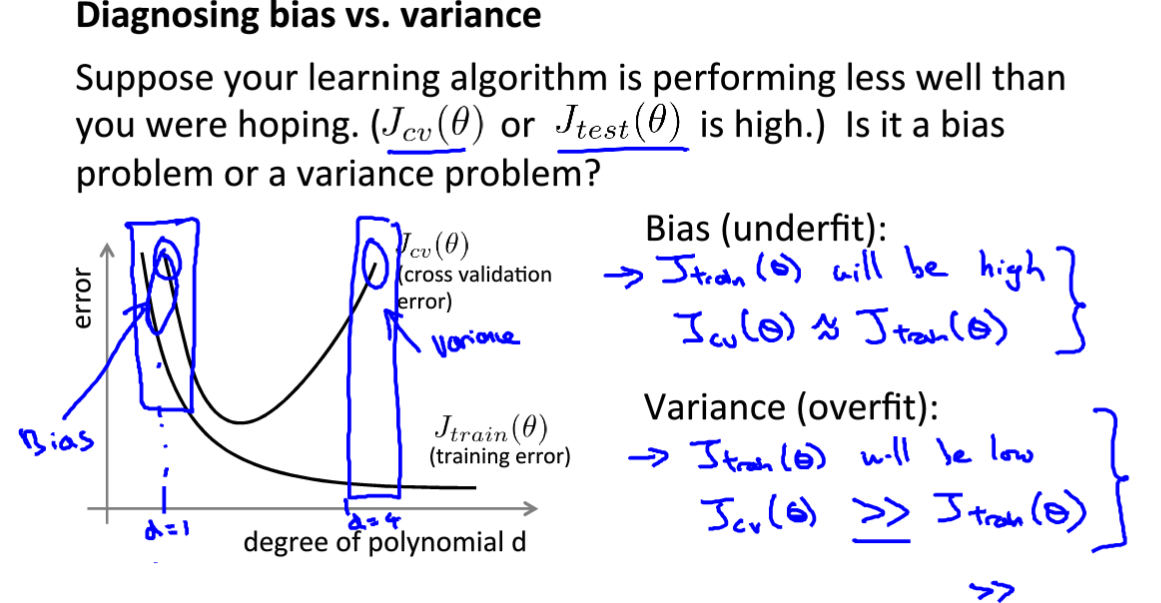
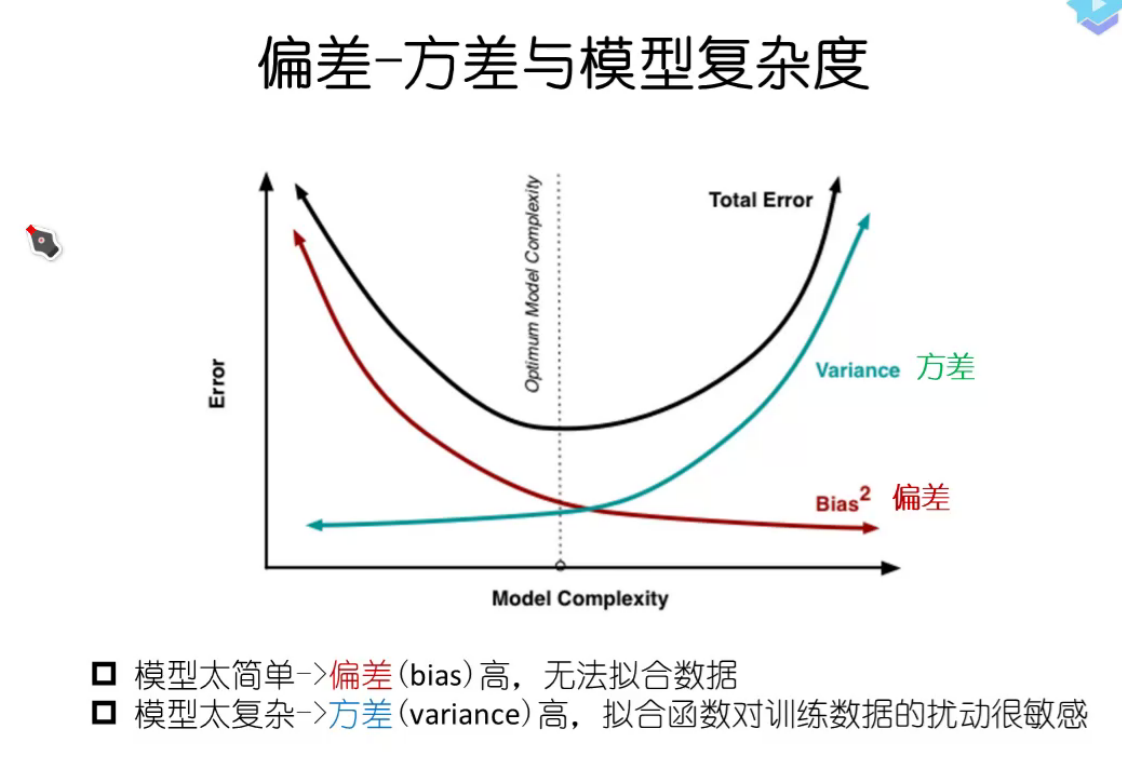
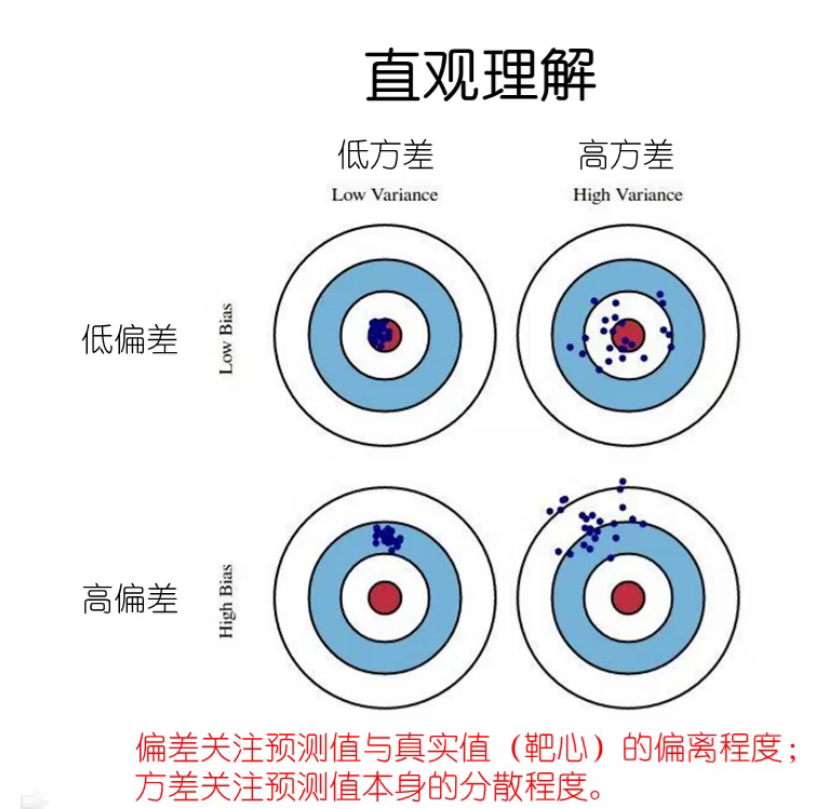
偏差与方差
偏差(与训练集数据拟合程度),方差(与验证集数据拟合程度)
项数少 :高偏差,高方差
项数多:低偏差,高方差
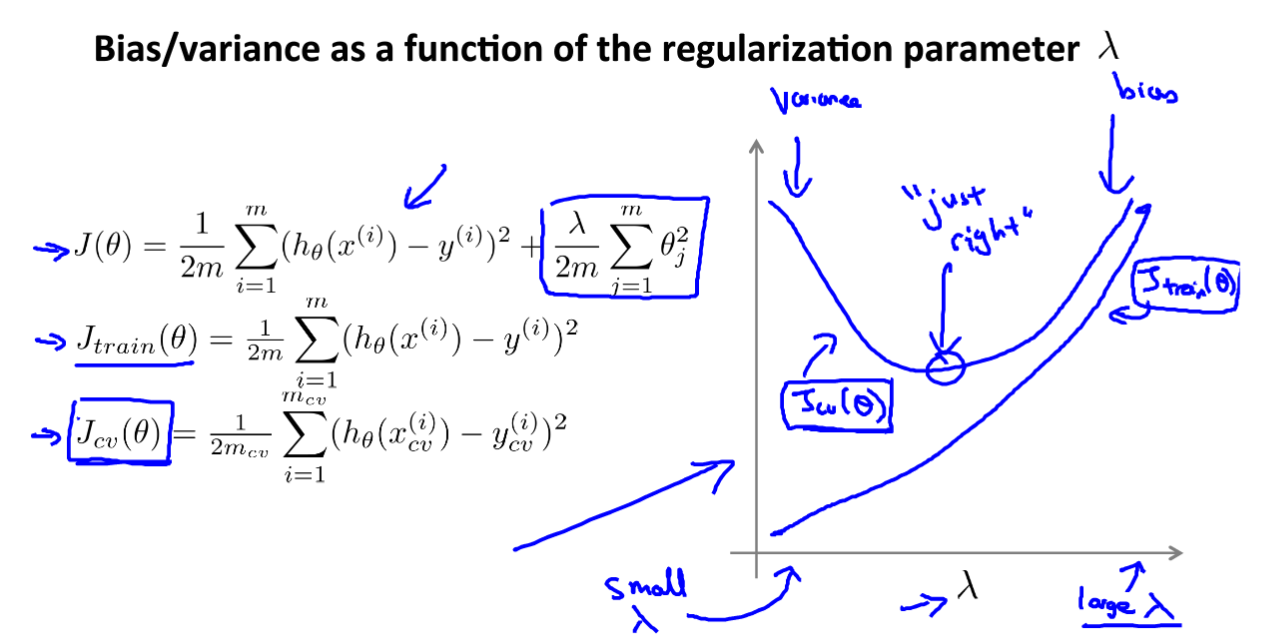
正则化:防止过拟合
lambda 小 :低偏差,高方差
lambda大:高偏差,高方差


学习曲线
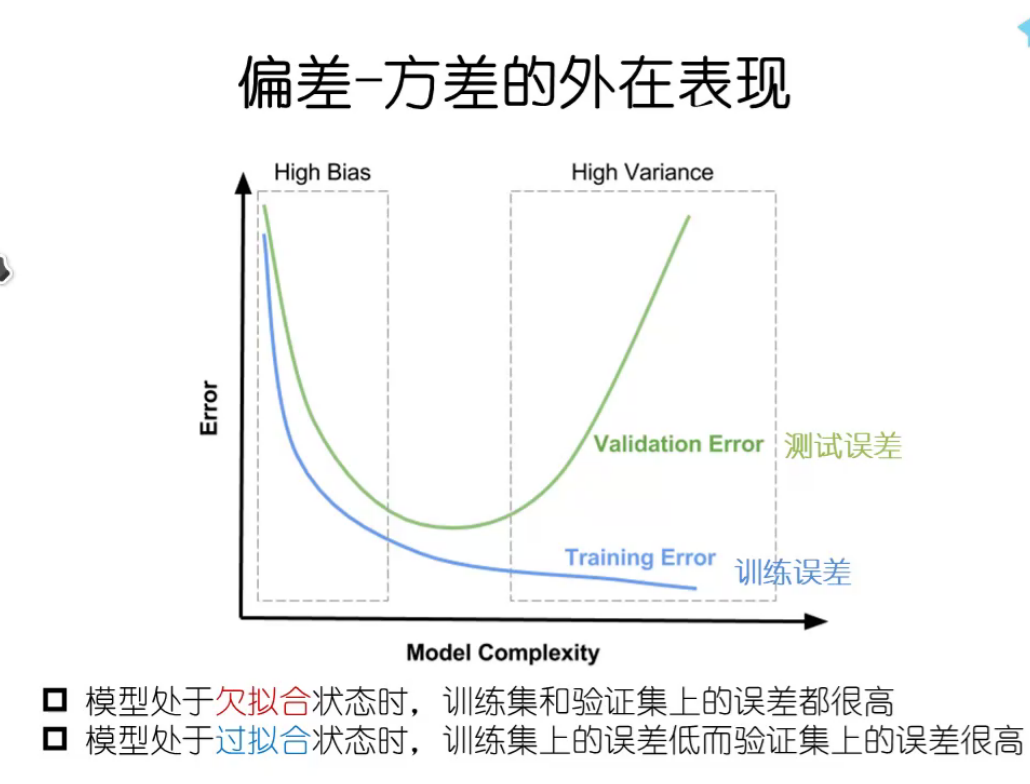
当模型高偏差时,加大训练集无用。
当模型高方差时,加大训练集可能有用。

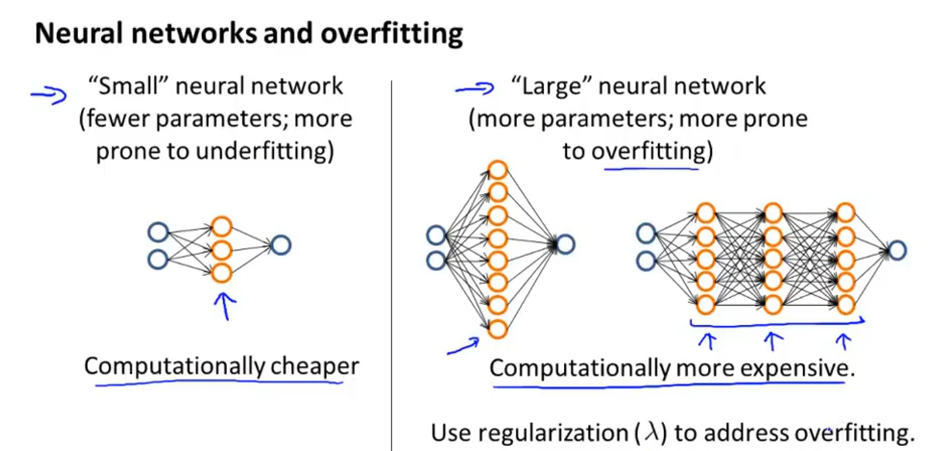
大型神经网络比小型神经网络性能要好
设计复杂学习系统
- 从简单的算法开始
- 绘制学习曲线
- 误差分析(验证集)
误差评估
偏斜类 skewed class (其中一类占比巨大。不对称性分类)
查准率 = 真的 / 预测真的
召回率 = 真的 / (实际是真的,预测真或假)
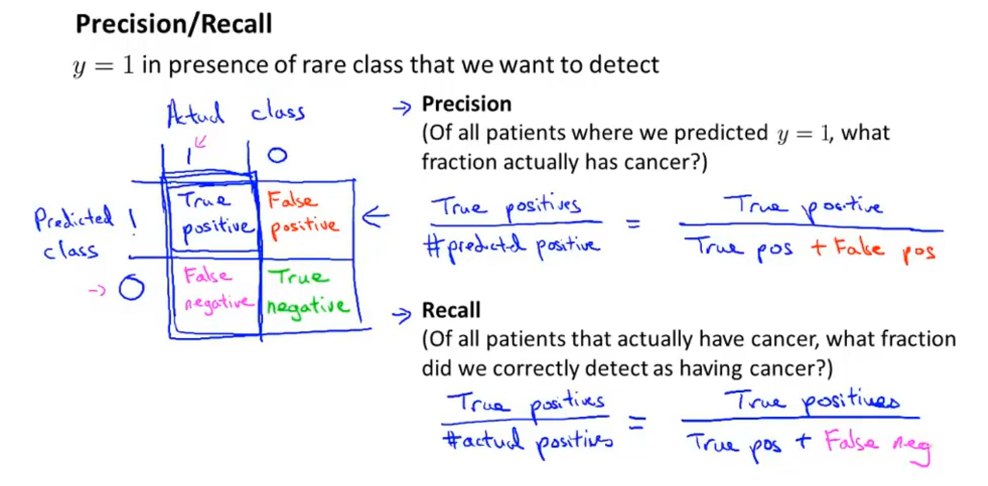
平衡查准率与召回率
F_1的值
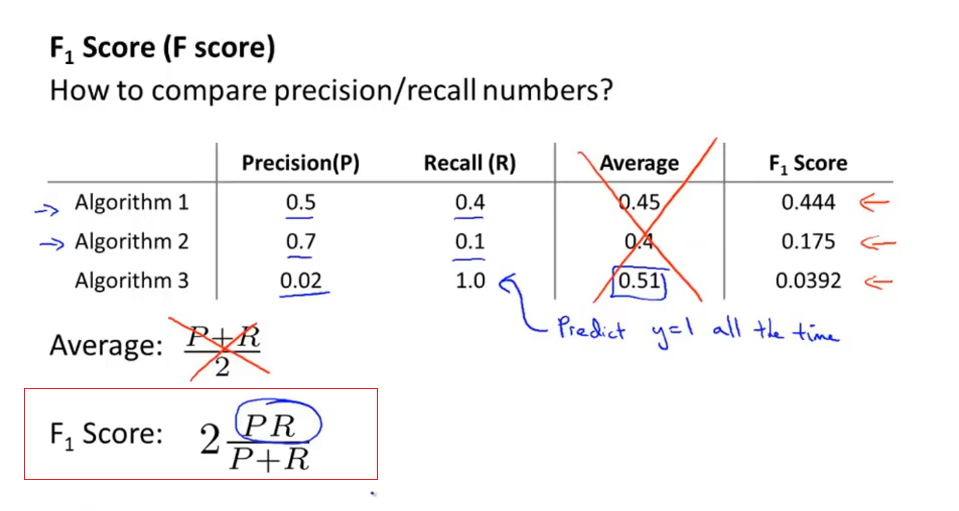
综合:

机器学习数据
大量数据 适合 大量参数的模型
编程作业
linearRegCostFunction.m
1 | function [J, grad] = linearRegCostFunction(X, y, theta, lambda) |
learningCurve.m
1 | function [error_train, error_val] = ... |
polyFeatures.m
1 | function [X_poly] = polyFeatures(X, p) |
validationCurve.m
1 | function [lambda_vec, error_train, error_val] = ... |